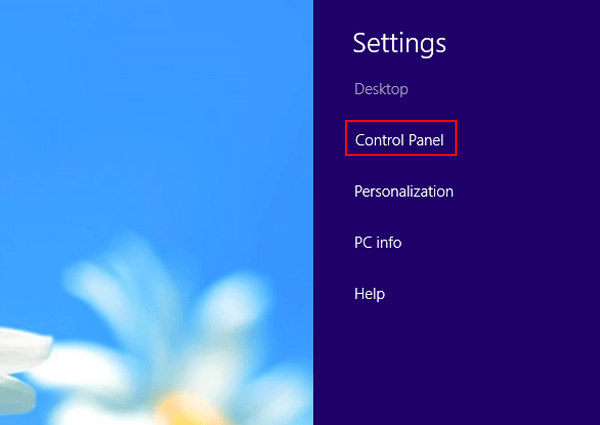
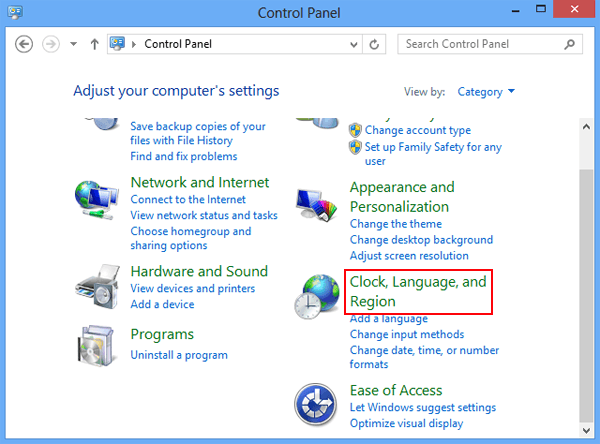
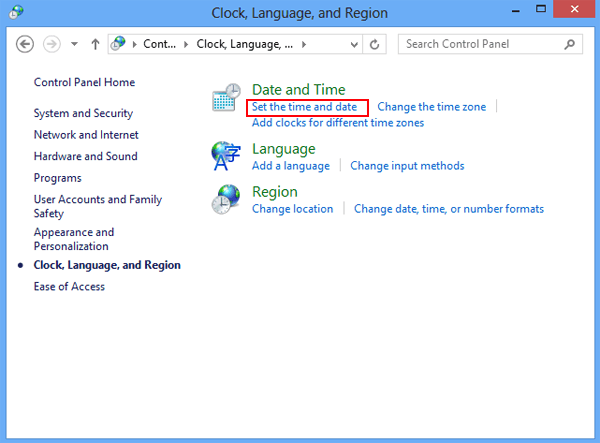
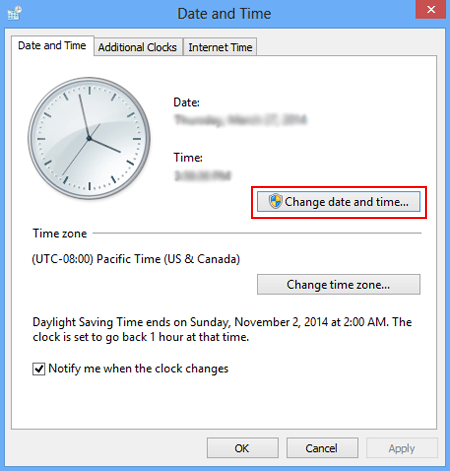
DOWNLOAD THE PDF THIS NOTES CONTACT THIS NO:- 8435646486
MS Word
Word Processing is perhaps the most common and comparatively easier application to work on any computer. A word processor lets you to change words or phrases, to move whole sections of text from one place to another, store blocks of text, align margins all in few seconds. Use of word processors has changed the look of official correspondence, reports, and proposals etc. to a great extent. MS Word is an advanced word processing product by Microsoft company. The powerful features of Word will allow you to create even graphic based multicolumn publications such as Fliers, News letters and Internet web pages.
This section provides an overview of MS – Word and deals with the following features:
Starting MS-WORD-2003 File management Editing documents Formatting documents Printing documents Inserting pictures into document Tables Password protect of document Inserting objects of other type(MS-Excel, Photo Editor etc.) Other features Mail merge
Start Word 2003
Switch on your computer. Click Start button then point to Programs and then click on MSWord. You will get a screen as shown below:
MS WORD Page 2 of 40
PARTS OF WORD WINDOW
Please see the picture below for a visual image of parts of an active window has:
Title bar This tells you which application package is currently running and which document is currently open.
Menu bar This is the traditional windows style drop-down menu. When you point to any menu title and click once with the mouse, the menu will open displaying all the commands available under this menu. Clicking on the desired command would tell Word to execute that command. Some commands have ellipses (…) in front of them. These commands have further sub commands. Commands appearing in dim mode cannot be executed unless the prerequisite functions required by that command have been performed, e.g. you cannot use the Copy or Cut command from the Edit menu unless you have selected a piece of text first. Many commands also have a keyboard shortcuts specified against their names.
Standard toolbar Toolbars contain buttons, drop-down menus and other controls that help you to quickly alter the appearance and arrangement of documents by executing a variety of word commands. Toolbars are very helpful and convenient in quickly executing
MS WORD Page 3 of 40
commands without having to go through menus. The standard toolbar contains icons for basic functions like opening files, saving files, printing files, cut, copy, paste etc.
Formatting toolbar This contains icons for changing the look of your text (called “formatting” in computer jargon); for example, there are icons for changing fonts, styles, font sizes, text alignment etc.
Ruler The Ruler lets you make changes to margins and indents, and helps you create document as per dimensions required.
Scroll tools These helps you travel within your document. You can go anywhere, up and down, right and left in your document mainly by two ways: Using the horizontal and vertical scroll bars with the help of the mouse; Or using the keyboard to press PgUp, PgDn, Home, End and arrow keys.
Status bar Also called the Status Area, this is the normally the last line on your screen. This gives the following information about your work—
• Current Page • Section Number • Current/Total pages in the document • Current Cursor Position (where the cursor is presently located) • Current Line Number • Current Column Number • Record Macro-whether macro recording is On or not • Track Revision-whether revisions have been made or not • Extend Selection • Over type mode-whether you are in Insert mode or overwrite mode
Cursor Also called the Insertion Pointer, this denotes the place where text, graphics or any other item would be placed when you type, overwrite or insert them. This looks like a tall, skinny toothpick and keeps blinking so that you can locate it easily.
Mouse pointer When your mouse pointer looks like an I-beam you should be able to move it freely on the screen. This is used for either placing the cursor at the desired place (take the mouse pointer there and click) or choosing any command either from the menu or from toolbars. The mouse pointer changes shape when in the process of doing certain tasks and the cursor disappears.
MS WORD Page 4 of 40
TOOLBARS AND THEIR ICONS
Word Standard Toolbar
MS WORD Page 5 of 40
MS WORD Page 6 of 40
MS WORD Page 7 of 40
File management
Creating a New Document
Click on File Menu Select and click New option
Otherwise click button on the standard toolbar
Opening an Existing Document:
Click File Menu Select and click Open option Otherwise click button on the Standard toolbar. Double click on the file from the open window
Saving a Document
Click File Menu Select and click Save button. Otherwise click button o on the Standard toolbar.
Moving through the document Open any word document. You can move the cursor to any location on the screen by using the arrow keys on the keyboard. Right arrow key is used to move one position to the right of the cursor Left arrow key is used to move one position to the left of the cursor. Up arrow key is used to move one position to the top of the cursor. Down arrow key is used to move one position to the down of the cursor. Page Up key is used to move down the screen at a time Page down key is used to move up the screen at a time Hold down Ctrl key and press Home to move to beginning of the document. Hold down Ctrl key and press End to move to end of the document.
MS WORD Page 8 of 40
You can move to any position on the screen by moving the cursor with the mouse. You can use scroll bars to scroll the text upward and down ward.
Closing a Document
Click File menu Select and click Close button. Otherwise click butt on menu bar
Editing Word document
Cut , Copy and Paste options
These options will allow you to Cut or Copy a piece of text from one location and to paste at a new location.
To do these functions,
Place the cursor at the begining of the text to be selected. Drag the mouse pointer over the text. The text will now appear in reverse vedeo as shown below:
Jawahar Knowledge Center
Click Edit menu and then click on Cut option (or) click icon on the Standard Toolbar. Move the cursor to the place where you want the text to be pasted.
Click Edit menu and then click Paste option (or) click icon on the Standard Toolbar.
For copying the text from one location to other location the same procedure is to be followed. The difference between Cut and Copy is that while using the Cut option the text will be removed from its original location and pasted at a new location, where as when using Copy option a copy of the selected text is pasted at new location without disturbing the original text.
MS WORD Page 9 of 40
Searching text
Open any document. Click Edit menu and then click Find option. You will get a screen as shown below.
In Find What text box type the word you want to find and then click Find Next button. Continue clicking Find Next button until you get the screen shown below.
Click OK button and then click X to close Find and Replace dialog box.
Replacing text
Open any word document. Click Edit menu and then click Replace option. You will get the dialog box as shown below and type the word with which you want to replace.
MS WORD Page 10 of 40
Click ReplaceAll button once. You get the below dialog box.
Click OK button and then click X to close Find and Replace dialog box.
Moving the cursor to a specific page
If your word document contains more than one page, you can directly go to specified page by clicking Edit menu and then clicking Go To option. You will get the dialog box as shown below.
MS WORD Page 11 of 40
In the Enter page number text box, type the required page number as shown below.
Click Go To button. Cursor will immediately jump to page 4. Click Close button to close Find and Replace dialog box.
Formatting documents
Bold, Underline and Italicize the selected text
Open a word document. Block the text by first clicking at the start of the text and holding the left mouse button and drag to the desired position and then release the left mouse button. The selected area will be highlighted. Move the mouse pointer to the button on the Standard Toolbar and click once. Move the mouse pointer outside your text and click to release the highlighting. Your text will now appear in BOLD FACE. Like this you can underline or italicize the desired text by using the following buttons
MS WORD Page 12 of 40
Left aligning, centering , right aligning and justifying text
Left Centre Right Justify
Open a word document. Block the text by first clicking at the start of the text and holding the left mouse button and drag to the desired position and then release the left mouse button. The selected area will be highlighted. Move the mouse pointer to Align Left button on the toolbar and click once. Your selected text will be left aligned. Move the mouse pointer to Align right button on the toolbar and click once. Your selected text will be right aligned. Move the mouse pointer to Center button on the toolbar and click once. Your selected text will be centered. Move the mouse pointer to Justify button on the toolbar and click once. Your selected text will be justified.
Creating Bulleted and Numbered list If a list of items are to be numbered automatically it can be done using Numbered List option
Ex: Microsoft Office consists of MS-Word MS-Excel MS-PowerPoint MS-Access MS-Outlook The above text is to be selected with mouse. Click on the Numbered List button on the toolbar
Move out of the text and click to release the highlighting. Your text will now look like this
1. MS-Word 2. MS-Excel 3. MS-PowerPoint 4. MS-Access 5. MS-Outlook
Now re-select the text Click the Bulleted List button on the toolbar.
MS WORD Page 13 of 40
The numbers should be replaced with bullets as shown below
• MS-Word • MS-Excel • MS-PowerPoint • MS-Access • MS-Outlook
Indenting Paragraphs
Select a paragraph with the mouse. Click on the Right (increase) Indent b button on the toolbar.
Leave the highlighting on and click once more on the Right Indent button. Click once on the Left Indent button. Your text should now be indented by one Tab stop. Each time you click, the paragraph is moved one tab stop.
Changing case of text
You can change the selected text into either UPPERCASE, lowercase, Title case or tOGGLE cASE
Highlight the text. Select the Format menu option Choose Change Case option. You will get the dialog box shown below.
From the list of options select UPPERCASE to convert lower case into uppercase
MS WORD Page 14 of 40
Indenting text with tabs
Type your name and address as you would at the head of a letter, but aligned with the left margin e.g.
K.Manohar H.No 10-334/3, V.P. Nagar, Malakpet, Hyderabad.
Move the cursor to the start of each line and press the Tab key. Just as with the right indent button, your text will move right. How much it moves will depend on the tab settings, which you can change in the Format, Tabs menu as shown below.
Font Controlling
To get different character styles we can change Font type Click on Format menu Select Font option. You will get the following screen.
MS WORD Page 15 of 40
You can set Font type, Font Style and Font size and Color of the selected text. Click OK button.
Note: The above options are also available on the Formatting Toolbar
Font style Font Type Font size Color
Creating column wise documents
Open any word document file. Click Format menu and click Columns option. You will get a screen as shown below:
MS WORD Page 16 of 40
In the Presets tab, select Two option to get below screen.
Click OK button. Your document will be converted to two-column document.
MS WORD Page 17 of 40
Spelling and Grammar Checking of word document
Open any word document. Click Tools menu and then click Spelling and Grammar option. You will get the below dialog box.
Note all words that appear red color in First box are spelling mistakes. If you want to accept the suggested word, in the second box click on Change. If not, click Ignore button. You can also add a word to the dictionary by clicking on the Add button. Continue this process until you get the dialog box, shown below:
Click OK button. Save your work when the spell-check is complete, so that the corrections are saved.
MS WORD Page 18 of 40
Printing document
Set Page Setup options
Click File menu Select and click Page Setup option. You will get the following screen.
Here you can set margins (top, bottom, right and left), paper size, paper source and layout. Click OK button.
Creating Header and footer
You can create header and footer that include text or graphics. For example, page numbers, the date, a company logo, the document’s title or file name, the author’s name, and so on. You can use the same header and footer throughout a document or change the header and footer for part of the
MS WORD Page 19 of 40
document. For example, use a unique header or footer on the first page, or leave the header or footer off the first page. You can also use different headers and footers on odd and even pages or for part of a document.
The Header and Footer tool bar is
To Create header or footer
Creating different footers or headers for even and odd pages
MS WORD Page 20 of 40
Preview document
Open any word document. Click File menu and then click Print Preview option. You will get a screen similar to this.
MS WORD Page 21 of 40
You won’t be able to read your text, as preview is just for checking the layout. If you move the mouse pointer into the page a tiny magnifying glass icon appears. If you click on this, it magnifies the selected page.
Press PgDn to move through your document if it is more than one page long.
If you need to make changes before printing, click the Close button to return to your document
Print document.
Click File menu Click Print option. You will get a screen shown as below.
In the above figure you can set default Printer name or you can select other printers from the drop down menu. You can set which pages to print, how many copies to print, the page range like ”1-3,5-7”, whether to print all pages and so on.
MS WORD Page 22 of 40
Before printing, make sure your printer is switched on, is loaded with the appropriate paper [A4], and is on-line. If you are satisfied with the layout of your document, click on the Print icon on the toolbar to obtain a printout. You should see a message on screen showing that your file is being prepared for printing. Click OK button.
Inserting pictures into the document
Inserting Clip arts Click Insert menu, click picture and then click Clip Art. You will get screen as shown below
Select the picture and then click Insert button. The selected picture will be inserted at the cursor position.
Inserting WordArt
Click Insert menu, click picture and then click WordArt. You will get a screen as shown below:
MS WORD Page 23 of 40
Select a WordArt Style format and then click OK button to get the below screen.
Here enter your own text ( for example type Welcome)and then click OK button.
MS WORD Page 24 of 40
Dragging Margins on the Ruler
Change to Page Layout view Choose View Ruler, if the ruler is not visible Point to transition area (where the grey area turns white) on the ruler. The mouse pointer changes to double headed arrow. Drag the margin to the desired position using the mouse. Watch the change in the Ruler’s dimension as you drag.
Page Breaks
Page Breaks are the places in your document where one page ends and a new page begins. Many things affect where page breaks will occur. Factors include the size of your paper, Margin setting, Paragraph Formats and section breaks. Page breaks appear as dotted lines in Normal view.
Forcing Page Breaks
Move cursor to the place of the break.
Choose Insert Break The Page Break dialogue box appears as below.
Click OK & the page break appears in the required position.
To insert page breaks press Ctrl+Enter. Page Break will be inserted at the place of the cursor.
MS WORD Page 25 of 40
Drop Cap Feature
Select the Paragraph then Click Format menu and then Click on Drop Cap then you will get a screen as shown below:
Now Select the required position for Drop Cap and click OK
Creating Tables
Tables are preferred when compared to using spacebar or tab for alignment to give a table format, but Word has another excellent feature for alignment called “Tables”. This feature is used to create financial reports, catalogues, accounts etc.
Tables consist of rows and columns. The text can be typed in the cells. The size, shape and appearance of a cell are controllable features. You can also convert a text to a table and a table back to text. It also supports importing and exporting data onto a spreadsheet.
To create a table using Insert Tables Button
Move the cursor to the place where you want to insert the table Choose tables button from the Standard Toolbar Drag the mouse to highlight the desired number of rows and
columns in the tables menu
MS WORD Page 26 of 40
Release the button. An empty table is inserted.
To create a table using table menu
Choose Insert table from Table Menu . You will find a dialog box as shown below:
Now type the Number of Columns and rows as you require and set column width Auto. So that the Column with will be equal to the width of the text. Now click OK.
An empty table is inserted in the document. Now inserting rows, columns, Deleting rows and widening the columns is very easy.
Insert Rows:
Place the cursor in the table, where rows are to be inserted Choose Table and click Insert Rows option to insert rows in the table
Delete Rows:
Select the Row which is to be deleted Click Table and click Delete cells option.
In the same way you can do with columns also
MS WORD Page 27 of 40
Using Formulae in the table
Tables can be used to prepare financial statements. Different functions can be used to calculate Column totals, Row totals, Average , Count, Minimum and maximum of given values etc. To use a formula in the table
Keep the mouse cursor at the place where the value has to come Click Table menu and then click Formula option.
You can see the following dialog box.
MS WORD Page 28 of 40
Then click OK button
If you don’t want the above function, then choose another from Paste function drop down list.
Sort the Table
We can arrange the data in the table in some order i.e. By name, By ID no, By basic etc.
To sort the table
Select the table by using menu Table -> Select table Sort the table by using menu Table -> Sort options
You will find the following dialog box:
Now select the sort by field and click OK
Numbering Pages
Open any word document. Click Insert menu and then click Page Numbers option. You will get the screen as shown below:
MS WORD Page 29 of 40
By default the page number is placed at bottom right corner within the page. You can change the position of the page numbers by selecting other options like “top of the page, center” from the Drop down List boxes. Choose the Format button to review the other page numbering options or choose OK button to set the changes made in the Page Numbering dialog box.
Auto correct
AutoCorrect stores a list of common typographical errors and their spellings. When you make an error, Word detects it and inserts the correctly spelled version of the word. You can add words to the AutoCorrect list, based on the mistakes you make. Look at the AutoCorrect dialog box.
MS WORD Page 30 of 40
Note that tm within parenthesis is automatically replaced by ™ with trademark symbol. To Add an AutoCorrect
Click Tools then click AutoCorrect, type the word in the place provided for Replace and With Options then click Add and then click OK. You can Delete an AutoCorrect option if you don’t want it.
AutoFormat
Use AutoFormat to reformat an entire document using a selected document template as a basis for the changes. Templates are supplied with Word, or you can create your own templates based on a document in which styles are applied to text, headings, lists and other text and graphic elements within the document. You can use Format/Style Gallery to view and apply available style templates to your document. Autoformat applies a style to every paragraph and heading. It typically replaces indentations created with spaces or tabs with paragraph indents, asterisks and dashes with bullets, and so on.
Auto Text
The AutoText feature lets you store commonly used passages, such as addresses, contract clauses, etc., and insert them whenever needed with a click of your mouse to create an AutoText entry.
Select a graphic or text block such as your name and address in your document.
Pick the Insert / AutoText menu selection: The Auto Text dialog box is displayed as shown below
MS WORD Page 31 of 40
Type a Short name in the Name box and click Add.
To use Stored Auto Text
Type the short name of your Auto text and Highlight it. Click Insert/ AutoText from menu and then click Insert . The text is inserted in place of the selected AutoText name.
To remove an AutoText item:
Pick Insert/AutoText to get the AutoText dialog box. Pick an AutoText name and click Delete and Close
MS WORD Page 32 of 40
Password Protecting the document
Open any word document. Click Tools menu and then click Options Click Security tab. You will get screen as shown below.
In the Password to open text box, type your password (Ex: type mahesh). Your password will appear as group of ***. Click OK button. You will get the following screen.
Reenter the same password and then click OK button.
MS WORD Page 33 of 40
Close the document by clicking File and then clicking Close option. Open the same document by clicking File and then clicking Open option. You will get a screen as shown below.
If you type the same password as earlier (mahesh) then only you can open the file. Enter the password and then click OK button. If you want to delete the password click Tools menu and then click Options. Delete the password in the Password to open text box. Click OK button. Your document will be unprotected.
Thesaurus The tools /Thesaurus menu selection gives you possible meanings and synonyms for selected words in your documents. This helps you be more precise in your writing. To use the Thesaurus, position the cursor in front of a word or highlight it. And Right Click and Then you will find a dropdown menu and select synonyms option select Thesaurus menu as shown below .
MS WORD Page 34 of 40
Lists of possible meanings and synonyms are displayed. Pick a desired word so that it is in the Replace with Synonym box and click the Replace button to use it. Use the Look Up button to find alternate meanings of a selected word in the Meanings box. Click Cancel to exit the Thesaurus dialog box without accepting any of the suggested changes.
Creating a Mail Merge document
Following are steps involved in creating a Mail Merge document.
Create a new data source and enter information Create the main document Insert fields into the main document. Merge data source and main document.
Creating a new data source
This file is created basically to store the information like addresses which is to be used to merge with the main document.
Open a New word document Create a Table with following information :
First Name Last Name Add1 Add2 Add3 Bhaskar Rambha Banjara Hills Road No.3 Hyderabad Ashok Reddy Kukatpally Main Road Hyderabad Ravi Kumar Gandhi Nagar RTC X Roads Hyderabad Save the file as address.doc and close.
Creating the Main Document
From the Tools menu Letters and MailingMail Merge.
In the Main Document area of Mail Merge Helper window click the Create button. Clicking on the down arrow opens the pull down menu.
MS WORD Page 35 of 40
Select Letters. and under Step 1 of 6, Click on Next : Starting document as shown in the above window (step 1).
You will get 3 options to select from the following window
• Use the Current Document • Start from a template. • Start from Existing Document
MS WORD Page 36 of 40
Select the first option : Use the current document
Type the letter leaving sufficient space to place addresses later
MS WORD Page 37 of 40
Now click on Write Your letter link (step 3) Then you will get following window.
Now Select an Existing Data Source i.e. the file address.doc and Click on Open Button.
Then you will get following window.
MS WORD Page 38 of 40
Click Ok.
Then you will see the following screen
• To add recipient information to your letter Click on More items and insert the fields wherever required.
After inserting fields your document may look like this :
MS WORD Page 39 of 40
Now see Step 4 of 6 and click on Next : Preview your letters
You can preview all the letters by clicking on Recipient 1..2.. so on
After Preview come to Step 5 of 6 and click on Next : Complete merge
MS WORD Page 40 of 40